- Last Updated On: September 13, 2024
High Blood Pressure: Treatment, Diagnosis & More
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding High Blood Pressure
- Signs and Symptoms
- Diagnosis of High Blood Pressure
- Immediate Treatment for High Blood Pressure at Home
- New Treatments for High Blood Pressure
- Emergency Treatment for High Blood Pressure at Home
- Long-Term Treatment for High Blood Pressure
- Conclusion
Did you know that nearly 1.28 billion adults aged 30–79 years have high blood pressure? This silent killer often goes undetected, quietly damaging your body for years before symptoms appear.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, occurs when the force of blood pushing against your artery walls is consistently too high. While it may not sound alarming, the consequences can be severe – ranging from heart disease to stroke.
The good news is that early detection can be a game-changer. By identifying and managing high blood pressure early, you can significantly reduce your risk of life-threatening complications.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into high blood pressure. From understanding its signs to exploring effective treatment for high blood pressure, we’ve got you covered.
Understanding High Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries as the heart pumps it around the body. It’s measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and recorded as two numbers:
- Systolic Pressure: The maximum pressure when the heart contracts.
- Diastolic Pressure: The minimum pressure when the heart relaxes and goes to a new contraction.
Normal blood pressure is equal to or slightly below 120/80 mmHg. High blood pressure is generally defined as:
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) |
| Elevated | 120-129 | <80 |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 130-139 | 80-89 |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | ≥140 | ≥90 |
High blood pressure puts extra strain on your heart and blood vessels, which increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other serious health issues.
Signs and Symptoms
High blood pressure, or hypertension, often shows no clear signs. This has led to its nickname as the “silent killer.” However, when signs do show up, they might include:
- Headache,
- Dizziness,
- Nosebleeds,
- Trouble Breathing,
- Chest Pain,
- Changes in Sight,
- Feeling Tired,
Many people with high blood pressure don’t feel any different. If you have high blood pressure or you’re dealing with any of these signs, you should immediately consult with a healthcare professional.
Diagnosis of High Blood Pressure
Hypertension does not show up with prominent symptoms. Thus, the condition remains undiagnosed for many patients. However, once you observe any associated symptoms, then a medical diagnosis is essential for confirmation and timely treatment. Diagnosing high blood pressure usually involves the following steps:
- Medical History
The healthcare provider will first review your medical history, including any symptoms, family history of hypertension, and lifestyle, such as diet, exercise, and smoking habits. This will help them better analyze the cause.
- Physical Examination
In the next step, your doctor will perform a physical exam to check for signs of hypertension-related complications, such as heart disease or kidney issues. They may also look for some injury that might be causing a sudden higher rate of blood flow in the vessels.
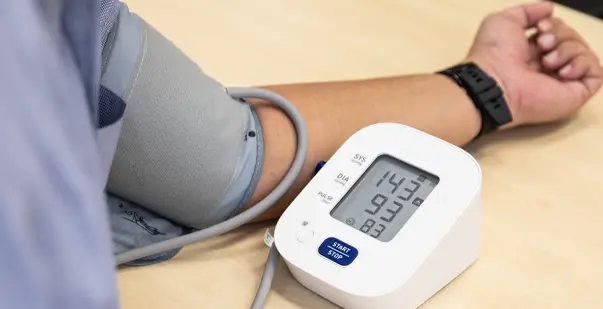
- Blood Pressure Measurements
Your healthcare provider will then take multiple readings over time. These readings are taken over two numbers: systolic (the pressure when the heart beats) and diastolic (the pressure when the heart rests between beats).
If the reading shows results near 120/80 mmHg, then your blood pressure is normal. However, hypertension is generally diagnosed if readings are consistently 130/80 mmHg or higher.
- Additional Tests
Depending on the initial findings, your primary care physician will order further tests, such as blood, urine, or an electrocardiogram (ECG), to assess heart health or other underlying conditions that might be causing hypertension.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment for high blood pressure.
Immediate Treatment for High Blood Pressure at Home
When faced with a sudden spike in blood pressure, you have to look for immediate treatments for high blood pressure at home that can lower your blood pressure before some professional help arrives.
- Deep Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises have been proven to be effective for people dealing with hypertension. Slow, deep breathing can relax your blood vessels and lower blood pressure. You can try the 4-7-8 technique:
- Inhale for 4 seconds,
- Hold your breath for 7 seconds,
- Exhale slowly for 8 seconds,
- Repeat 4-5 times.
- Reduce Sodium Intake
You should avoid high-sodium foods and read labels to choose low-sodium options. Limiting sodium can help lower blood pressure by about 5 to 6 mm Hg. Reducing sodium intake is a great management strategy for hypertension.
- Healthy Diet Choices
People with hypertension must follow a healthy and balanced diet. Foods high in potassium, such as bananas, spinach, and sweet potatoes, can help balance sodium levels and lower blood pressure. They should also avoid junk and fast food and make a habit of eating home-cooked meals.
- Physical Activity
Regular exercise and physical activity are some of the best ways to manage hypertension at home. Take a brisk walk or do some light aerobic exercises. You should exercise for 150 minutes a week. For this, divide these minutes into 30-45-minute exercise sessions daily. Regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure and decrease the chance of cardiac arrest over time.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques
Stress can cause temporary spikes in blood pressure. To calm your mind and body, try meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery.
Note that these methods are for temporary relief and should not replace professional medical advice or prescribed treatments.
New Treatments for High Blood Pressure
Medical research continues to advance, bringing new treatments for high blood pressure to the forefront. Some innovative approaches include:
- Renal Denervation
This minimally invasive procedure uses radiofrequency energy to disrupt nerve signals between the kidneys and the brain, potentially lowering blood pressure. Along with this, cardiac massage is beneficial.
- Baroreceptor Activation Therapy
This innovative therapy involves a small device that activates carotid artery baroreceptors when implanted inside it. These receptors play a role in maintaining normal blood pressure in human beings. The person’s body mechanisms to lower blood pressure are turned on after an electrical impulse reaches these cells from the implant.
- Central Iliac Arteriovenous Anastomosis
This surgical technique directly connects an artery and a vein within the pelvis, thereby reducing overall blood pressure. It is particularly used among patients with refractory hypertension, which does not respond well to treatment plans such as medication or lifestyle changes.
Always consult with your healthcare provider about the most appropriate treatment options for your specific situation.
Emergency Treatment for High Blood Pressure at Home
In cases of severely elevated blood pressure (hypertensive crisis), emergency treatment for high blood pressure at home may be necessary. However, it’s crucial to understand that true hypertensive emergencies require immediate medical attention. If you experience symptoms such as severe headache, vision changes, chest pain, or difficulty breathing, along with very high blood pressure, call emergency services immediately. For less severe situations, you can try these steps:
- Take Prescribed Medications: If you have been prescribed blood pressure medications, take them as directed by your doctor.
- Rest and Relax: Lie down and rest in a quiet, dark room for 15-20 minutes.
- Use Cold Compresses: Apply a cold, damp cloth to your forehead or neck to help lower body temperature and promote relaxation.
- Avoid Stimulants: Stay away from caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, which can elevate blood pressure.
- Practice Mindfulness: Use mindfulness techniques or guided meditation apps to help reduce stress and anxiety.
These measures are temporary and should not replace professional medical care. If your blood pressure remains dangerously high or you experience concerning symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Long-Term Treatment for High Blood Pressure
Effective long-term treatment for high blood pressure typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. The goal is to bring your blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg and maintain it healthily. It typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication management. Here’s a brief overview of effective strategies:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing blood pressure over the long term:
- Diet: Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan is particularly effective in lowering blood pressure.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce blood pressure. Even a modest weight loss can have a positive impact.
- Limit Alcohol and Sodium: Reducing alcohol intake and limiting sodium consumption can help control blood pressure levels.
- Quit Smoking: Stopping smoking improves overall cardiovascular health and can lower blood pressure.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help manage stress, which may contribute to high blood pressure.
2. Medication Management
When lifestyle changes are insufficient, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to help control blood pressure. These medications can include:
- Diuretics: Help eliminate excess sodium and fluid from the body.
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Relax blood vessels by blocking certain hormones.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, allowing them to relax.
- Beta-Blockers: Reduce heart rate and the force of heart contractions.
Final Thoughts
High blood pressure is a serious condition that requires attention and proper management. If it worsens, hypertension can cause respiratory or cardiac conditions, which may require people to be trained in CPR and the use of AEDs. Additionally, immediate treatment for high blood pressure at home can provide temporary relief. However, these measures are not a substitute for professional medical care.
Persistent high blood pressure requires medical evaluation and a long-term management plan crafted by a healthcare provider. For long-term management and well-being, commit to a thorough treatment plan complemented by a healthy lifestyle.
Read More: